Sugar often gets a bad rap, yet despite the negative press and consistent studies bashing it, it remains a fundamental source of energy for our bodies. While natural sugars found in fruits and dairy products are less concerning due to the accompanying fiber and nutrients, refined sugars, like the ones in processed foods, pose significant health risks. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, the average American consumes a concerning amount of added sugars daily.1 But consuming too much sugar goes beyond mere extra calories:
1. Increased Hunger/Weight Gain

Having too much sugar can lead to increased feelings of hunger due to its lack of satiating nutrients such as protein and fiber. This can result in overeating and eventual weight gain.
2. Acne and Wrinkles
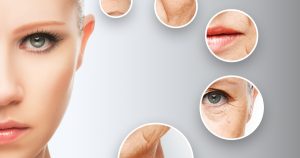
Too much sugar has been linked to skin issues like acne and premature aging. Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to inflammation and hormonal imbalances, which only further perpetuate skin conditions and accelerate wrinkle formation.2
3. High Blood Pressure

Research suggests a correlation between too much sugar consumption and elevated blood pressure levels. The link has primarily been sourced from sugary drinks (sorry Coca-Cola). This increases the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular problems.3
4. Sleep Issues

A high-sugar diet can disrupt both sleep patterns and sleep quality. When your blood sugar levels fluctuate, it can lead to issues falling asleep or staying asleep, which makes sleep overall inconsistent.
5. Joint Pain

As mentioned earlier, too much sugar can trigger inflammation in the body, which can also create joint pain. People with a condition like arthritis may experience an increase in discomfort from high levels of sugar. They would benefit from a more balanced diet.
6. Cavities

This one is more of a no-brainer. Sugar feeds bacteria in the mouth, leading to the production of acids that erode tooth enamel and promote the formation of cavities. If you have too much sugar you can increase the risk of dental decay.
7. Fatigue and Low Energy

While sugar provides a quick energy boost, it is often followed by a crash in energy levels. Rapid fluctuations in blood sugar can leave individuals feeling fatigued and low on energy, especially when consumed in excess. To offset this, more is introduced to try and maintain that high blood sugar feeling, leading to too much sugar overall. It is also a trap, as the body remains hungry, and while your blood sugar spikes, your energy levels do not.
8. Irritability

Sugar consumption, in general, can impact mood stability by causing rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels. This may lead to irritability and mood swings as the body struggles to regulate glucose levels. Think of someone ‘hangry’ but on a cellular level: that’s what happens when you have too much sugar.
9. A Cravings for Sweets

Sugar activates the brain’s reward system, which the brain quickly learns to seek more of. Too much sugar offsets the brain’s ability to naturally source or earn these rewards and creates a cycle of cravings – leading to overconsumption.
10. Foods Don’t Taste Sweet Enough

When you eat too much sugar, it desensitizes your taste buds, reducing the natural taste of sweetness in foods. You may find the need to consume even sweeter foods to satisfy a craving, which only leads to, you guessed it, greater sugar consumption.
The Bottom Line

The negative side effects of excessive sugar consumption extend far beyond mere weight gain. From mood swings to sleep issues and increased health risks, having too much sugar negatively impacts you from all sides. It is essential to be mindful of how much sugar is in your diet. Opt for whole foods over processed ones, and prioritize a balanced diet. Being aware of the signs is the first step towards better health and overall well-being.


